The Indian Constitution contains various schedules that provide additional details, lists, and instructions related to different aspects of governance and administration. Here is a summary of the schedules in the Indian Constitution:
- Schedule 1: Lists the States and Union Territories of India along with their respective territories. It provides a geographical demarcation of India’s political divisions.
- Schedule 2: Contains the forms of oaths or affirmations that various constitutional functionaries, such as the President, Governors, Members of Parliament, and others, are required to take before assuming their respective offices. These oaths emphasize their commitment to uphold the Constitution.
- Schedule 3: Provides the forms of oaths or affirmations for judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts. These oaths signify their commitment to impartially administer justice and uphold the Constitution.
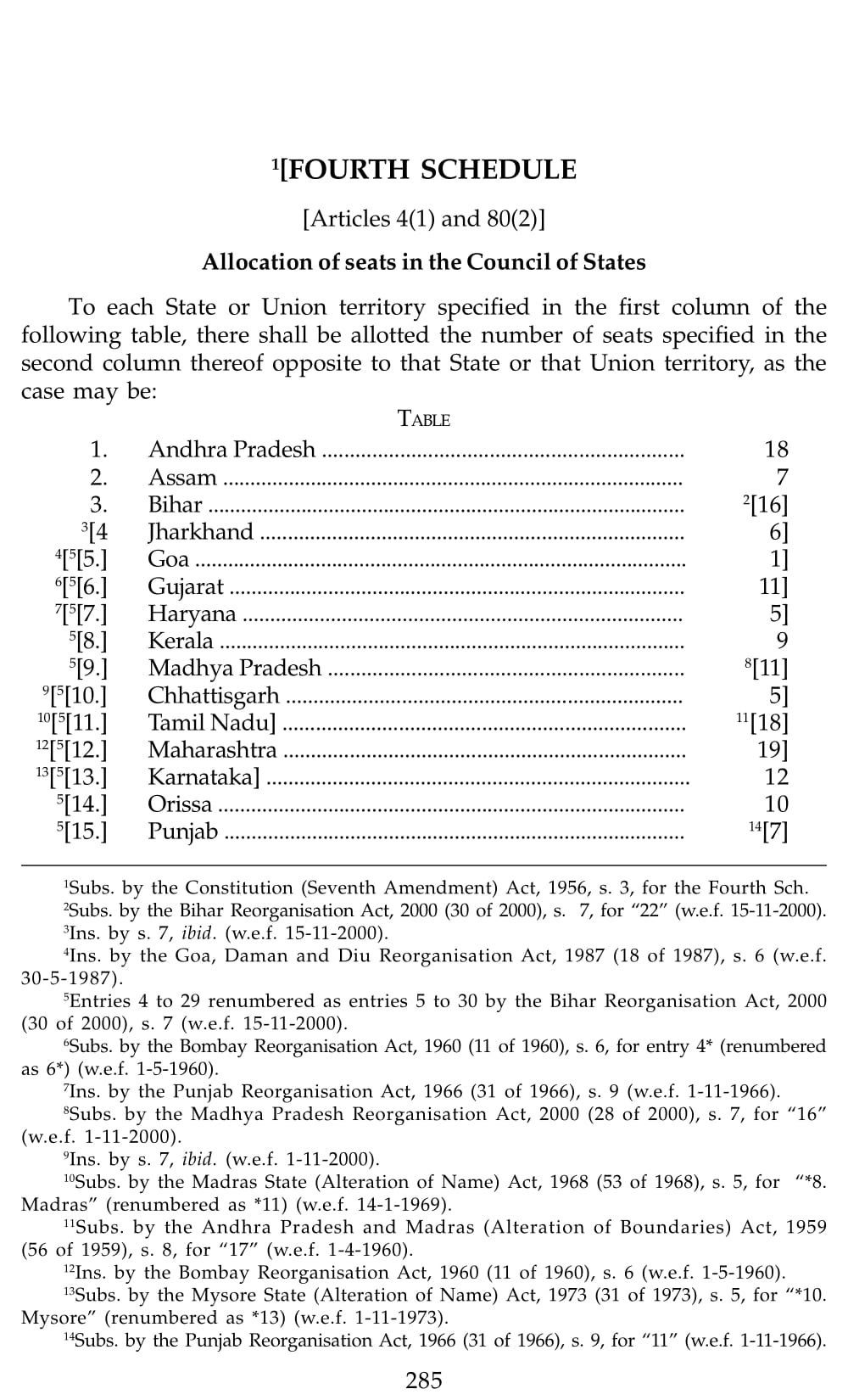
- Schedule 4: Specifies the allocation of seats in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) to each state and Union Territory. It determines the number of representatives each state or Union Territory can send to the Rajya Sabha.
- Schedule 5: Deals with the administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in certain states, including Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram. It provides a framework for local self-governance in these areas.
- Schedule 6: Covers the administration of tribal areas in northeastern states, including Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram. It allows for the establishment of autonomous district councils and regional councils to ensure self-governance.
- Schedule 7: Divides legislative powers between the Union (central government) and the States (state governments) of India. It categorizes subjects into three lists: the Union List (central government’s exclusive jurisdiction), the State List (state government’s exclusive jurisdiction), and the Concurrent List (shared jurisdiction).
- Schedule 8: Lists the languages recognized by the Constitution for official purposes. Different states may choose one or more of these languages for use in their official communications. It reflects India’s linguistic diversity.
- Schedule 9: Lists land reform laws enacted by various states. These laws are protected from judicial review on the grounds of violating fundamental rights. The schedule was included to promote agrarian reforms and equitable land distribution.
- Schedule 10: Contains provisions related to the disqualification of members of legislatures (both Parliament and state legislatures) on the grounds of defection. It aims to prevent legislators from switching parties without consequences.
- Schedule 11: It contains the provisions that specify the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats. It has 29 matters.
- Schedule 12: It deals with the provisions that specify the powers, authority and responsibilities of Municipalities. It has 18 matters.
These schedules collectively provide the framework for governance, administration, and the protection of rights in India. Please note that amendments and changes to the Constitution can occur over time, so it’s essential to refer to the latest official documents for any updates to the schedules.
These schedules play a significant role in providing additional details and structure to the Indian Constitution, covering topics such as governance, administration, language recognition, land reforms, anti-defection measures, and more. Please note that the Indian Constitution can be amended over time, so it’s essential to refer to the latest official documents for any updates or changes to the schedules.
List of Schedules of Indian Constitution, 1 to 12 Schedules of Constitution of India
- Schedule 1 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 2 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 3 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 4 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 5 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 6 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 7 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 8 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 9 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 10 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 11 Constitution Of India
- Schedule 12 Constitution Of India
PDF Download Schedules of Indian Constitution, 1 to 12 Schedules of Constitution of India
CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
The Constitution Of India Parts 1 to 22, Articles 1 to 395
Schedules of Indian Constitution & Articles
Aspirants should know about the Constitutional Articles related to the Schedules of the Indian Constitution. It will give them clarity of concepts and help them understand the chronology of important articles.
| Schedules of Constitution Of India | Articles of Constitution Of India |
| First Schedule | Article 1 and Article 4 |
| Second Schedule | Articles:
|
| Third Schedule | Articles:
|
| Fourth Schedule | Article 4 and Article 80 |
| Fifth Schedule | Article 244 |
| Sixth Schedule | Article 244 and Article 275 |
| Seventh Schedule | Article 246 |
| Eighth Schedule | Article 344 and Article 351 |
| Ninth Schedule | Article 31-B |
| Tenth Schedule | Article 102 and Article 191 |
| Eleventh Schedule | Article 243-G |
| Twelfth Schedule | Article 243-W |
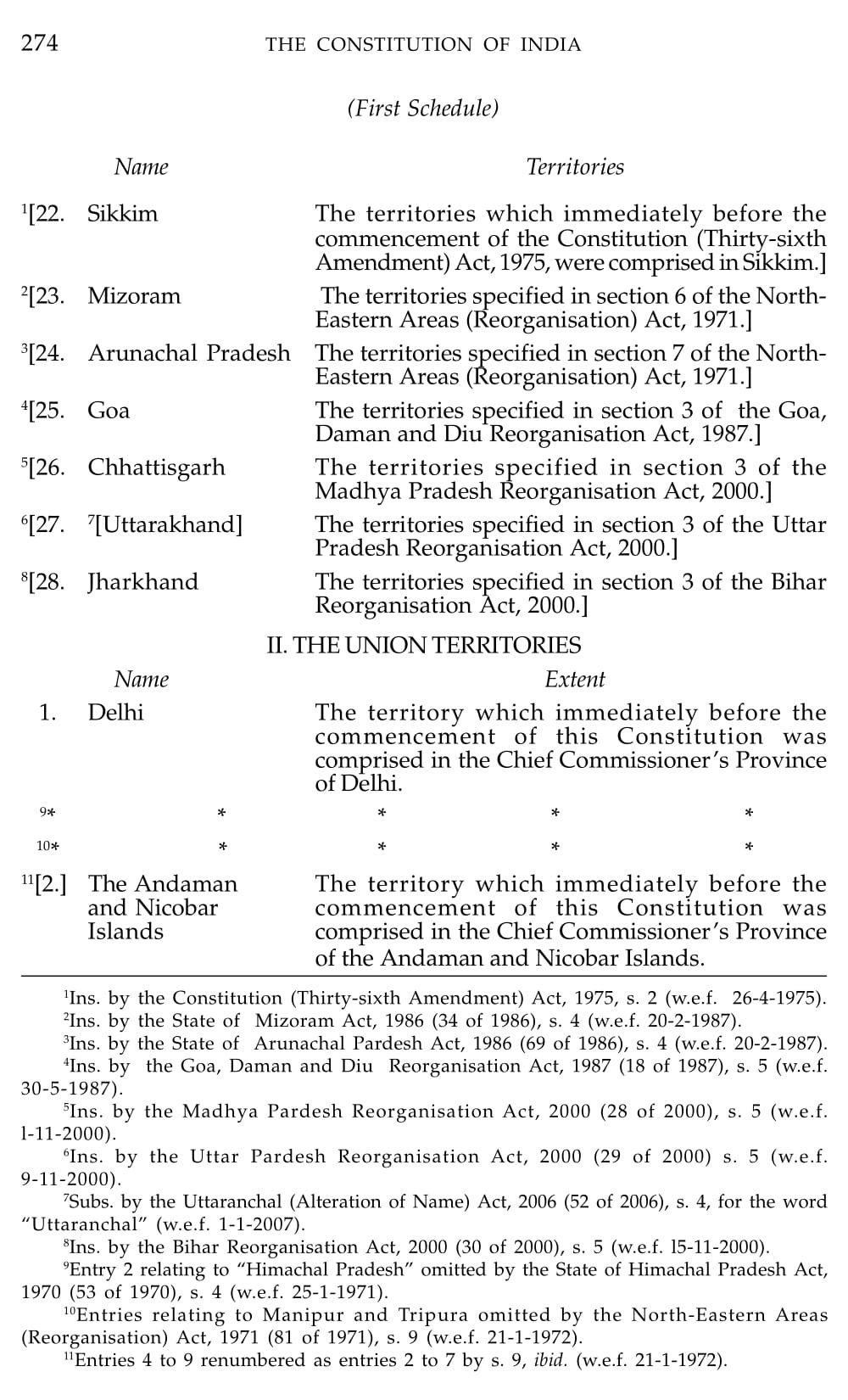
Schedule 1 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 1 Constitution Of India
Schedule 1 of the Indian Constitution lists the names of the States and Union Territories of India, along with their respective territories. It provides a comprehensive list of the political and geographical entities that make up the Indian Union.






Schedule 2 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 2 Constitution Of India
Schedule 2 of the Indian Constitution provides the forms of oaths or affirmations that are to be taken by various constitutional functionaries in India. These oaths or affirmations are typically administered during the swearing-in ceremonies of individuals who hold key positions in the government and other institutions.






Schedule 3 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 3 Constitution Of India
Schedule 3 of the Indian Constitution contains the forms of oaths or affirmations that are to be taken by judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts in India. These oaths or affirmations are administered to judges during their swearing-in ceremonies and are meant to ensure their commitment to upholding the Constitution and performing their judicial duties impartially.



Schedule 4 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 4 Constitution Of India

Schedule 5 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 5 Constitution Of India
Schedule 5 of the Indian Constitution contains provisions related to the administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in various states of India. These provisions are meant to protect the interests and promote the welfare of the scheduled tribes (indigenous communities) living in these areas. Schedule 5 deals specifically with the administration of tribal areas in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.




Schedule 6 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 6 Constitution Of India
Schedule 6 of the Indian Constitution contains provisions related to the administration and governance of tribal areas in the northeastern states of India. These provisions are meant to protect the interests and promote the welfare of the tribal communities (scheduled tribes) living in these areas. Schedule 6 deals with the administration of tribal areas in the following states:
- Assam: Parts of Assam, primarily the areas inhabited by tribal communities like the Bodos and the Karbis, are covered under Schedule 6.
- Meghalaya: The entire state of Meghalaya is covered under Schedule 6.
- Tripura: Certain areas in the state of Tripura, inhabited by tribal communities, are covered under Schedule 6.
- Mizoram: The entire state of Mizoram is covered under Schedule 6.
Schedule 7 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 7 Constitution Of India
Schedule 7 helps define the respective legislative powers of the Union and the States, ensuring a clear demarcation of authority in the governance of the country. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the federal structure of the Indian Constitution and ensuring the distribution of powers between the central and state governments.















Schedule 8 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 8 Constitution Of India
Schedule 8 of the Indian Constitution lists the languages recognized by the Constitution for use in various official purposes. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule. These languages are recognized for official communication at the central and state government levels. Here is the list of languages recognized in Schedule 8:
- Assamese
- Bengali
- Bodo
- Dogri
- Gujarati
- Hindi
- Kannada
- Kashmiri
- Konkani
- Maithili
- Malayalam
- Manipuri
- Marathi
- Nepali
- Odia (Oriya)
- Punjabi
- Sanskrit
- Santali
- Sindhi
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Urdu
Each of these languages has a special status for use in specific regions or states of India, based on the linguistic diversity of the country. The Constitution allows for the use of these languages in legislative proceedings, court proceedings, and other official communications.

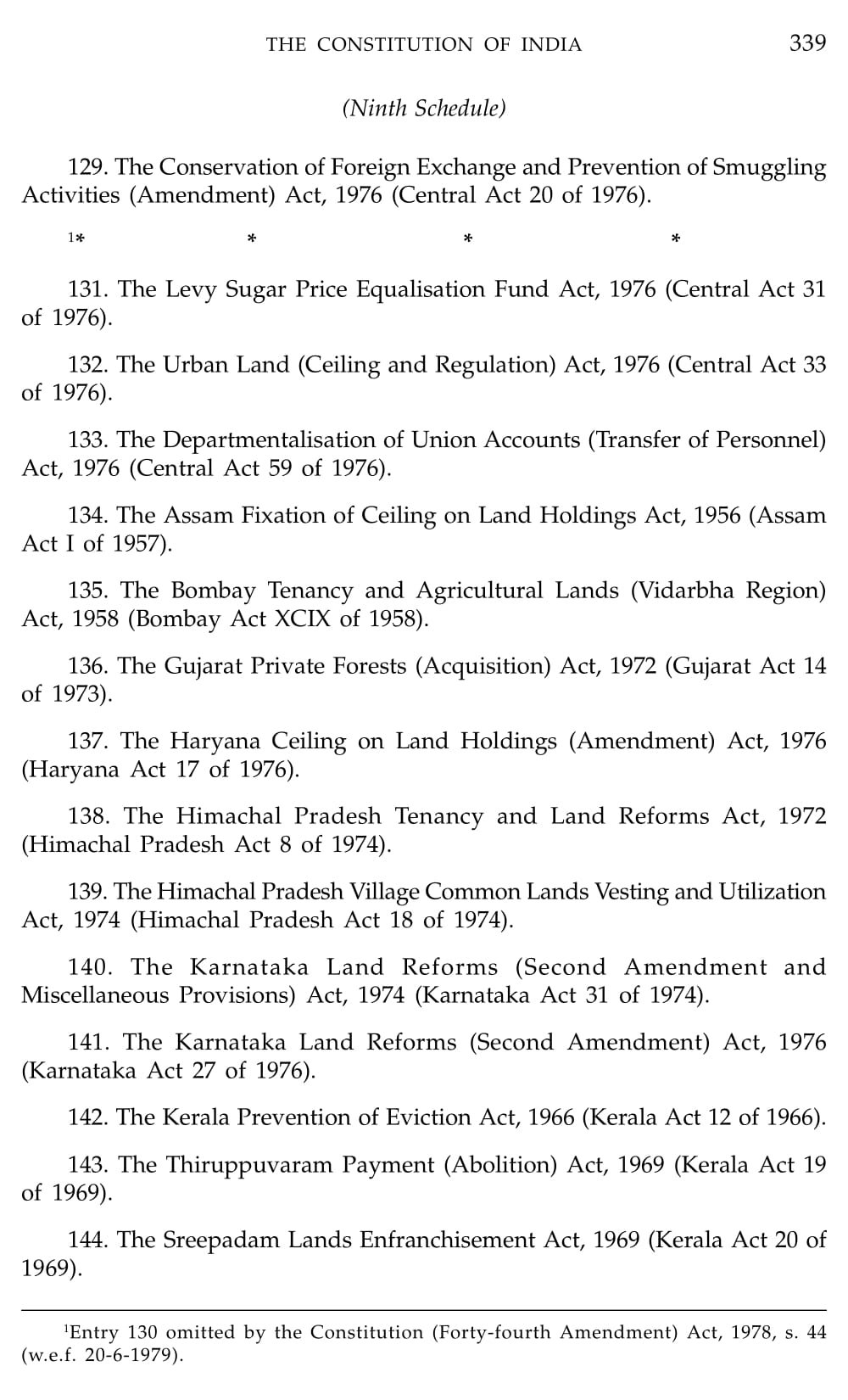
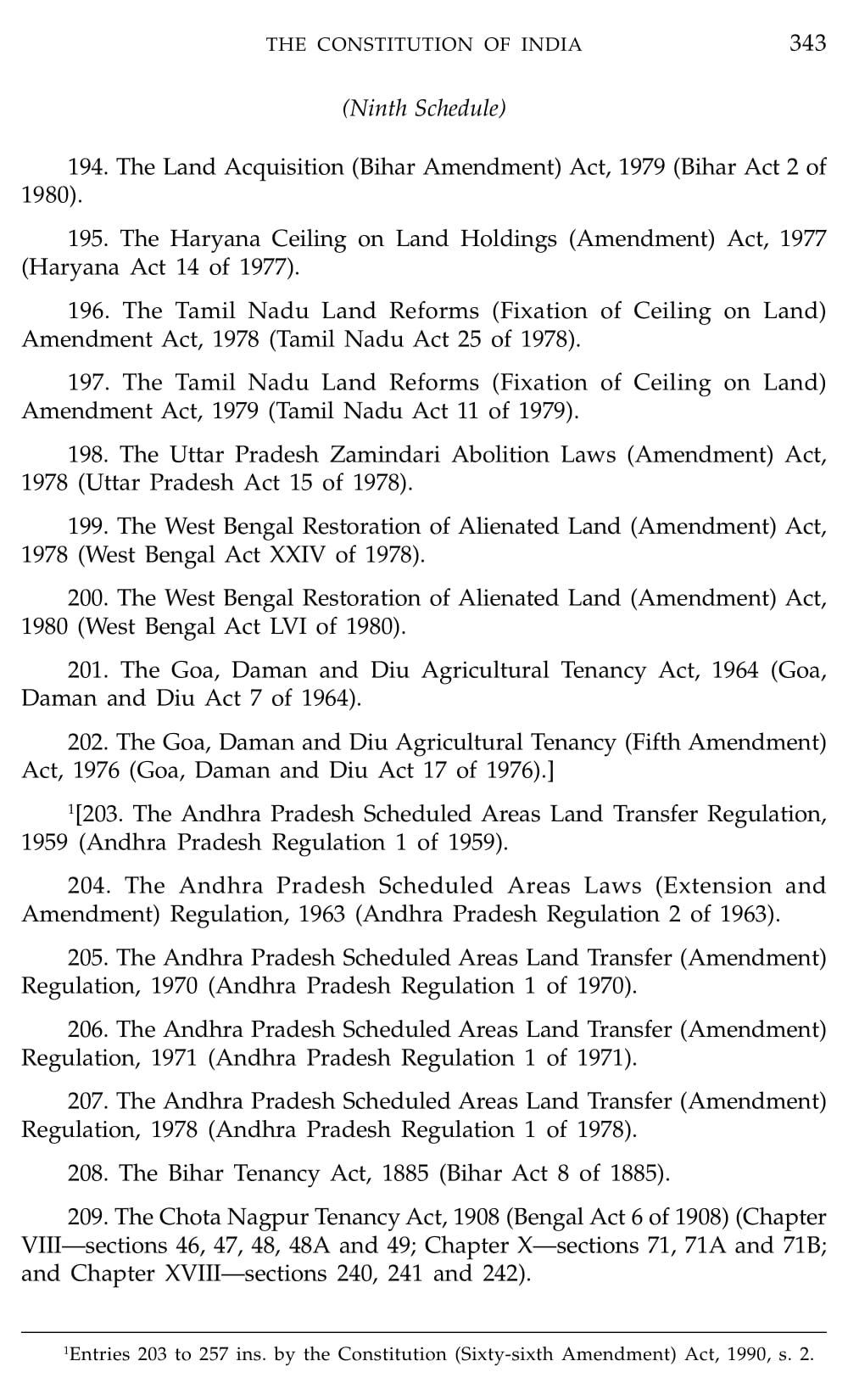
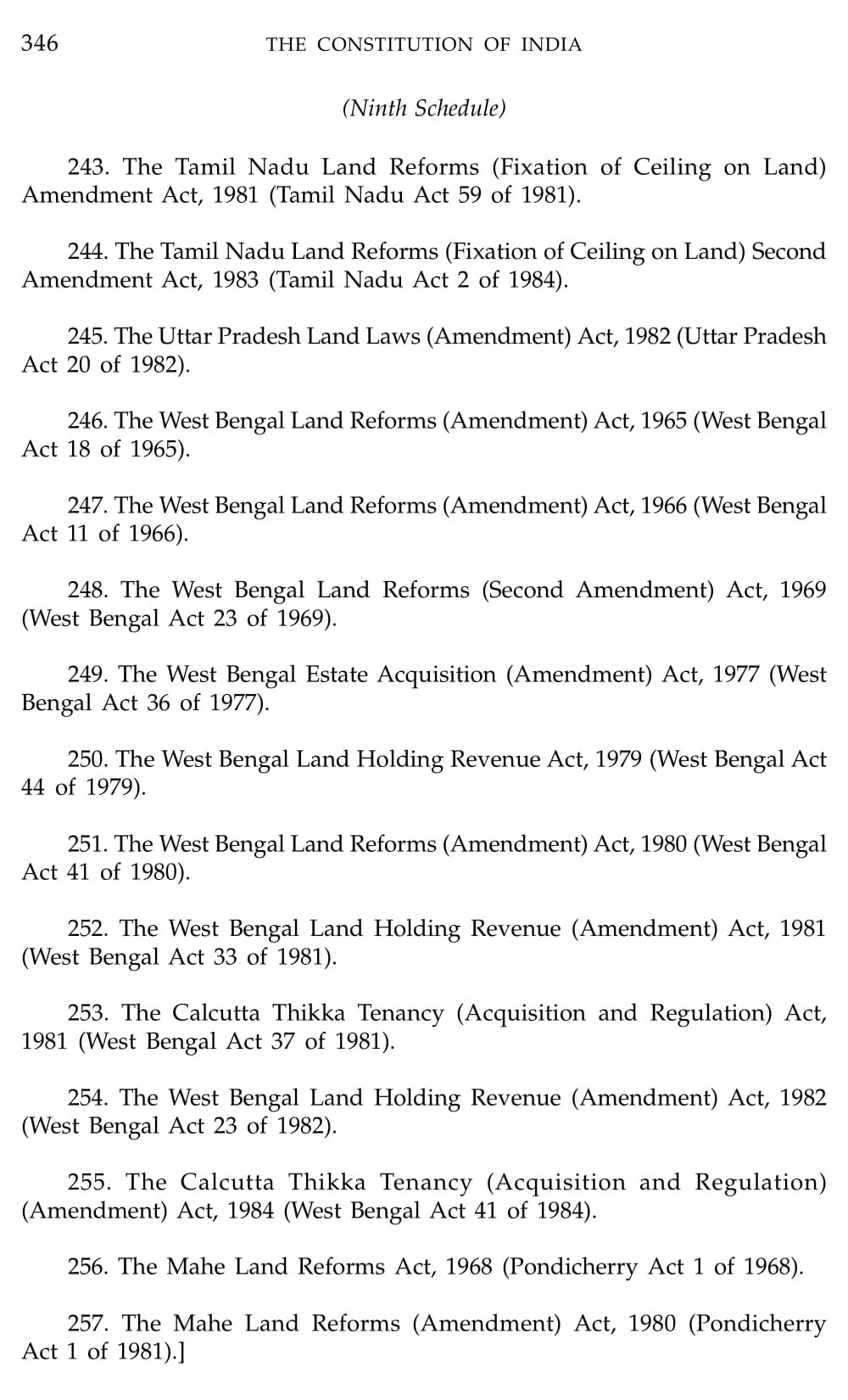
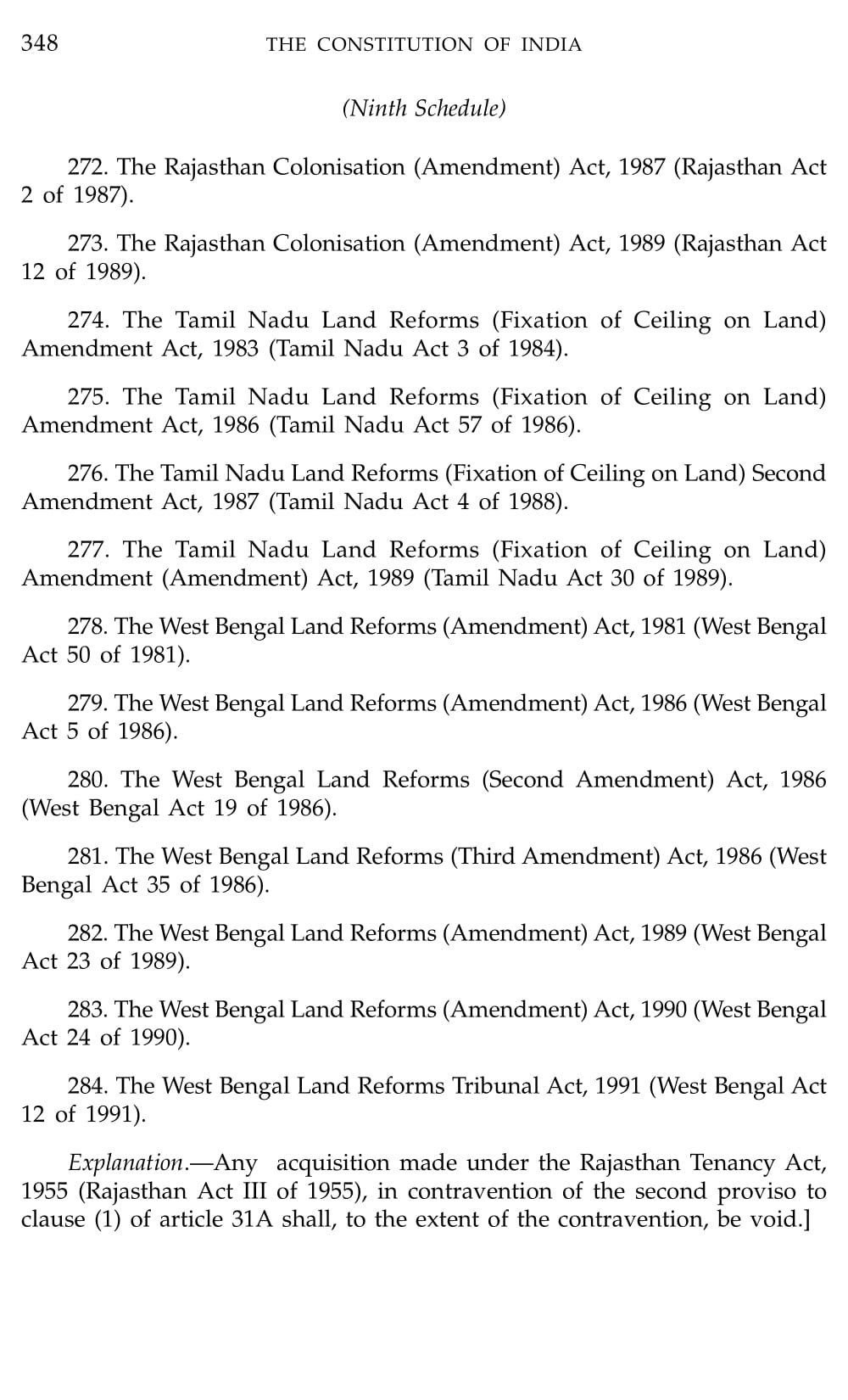
Schedule 9 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 9 Constitution Of India
Schedule 9 of the Indian Constitution contains provisions related to land reforms. It lists various laws that were enacted by different state governments to implement land reforms and abolish or regulate the system of landownership, including tenancy and other related matters. These laws were placed in Schedule 9 to provide them with protection from judicial review and legal challenges on the grounds of violating fundamental rights.














Schedule 10 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 10 Constitution Of India
Schedule 10 of the Indian Constitution deals with the provisions related to disqualification of members of legislatures on the ground of defection. It sets out the rules and procedures for disqualifying a legislator who changes party allegiance or engages in other activities that can be considered defection. The aim of Schedule 10 is to curb the practice of legislators frequently changing party allegiance for personal or political gain, which can lead to instability in the functioning of legislatures. It seeks to ensure that members elected on the ticket of a particular party do not switch parties at will, undermining the integrity of the party system.





Schedule 11 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 11 Constitution Of India


Schedule 12 Constitution Of India
What is Schedule 12 Constitution Of India


























